304 Not Modified Responses
This document explains how 304 responses work, their benefits, and how Cloudflare's Smart Edge Revalidation enhances this process.
What is a 304 Not Modified Response?
A 304 Not Modified response is an HTTP status code indicating that the requested resource has not been modified since the last time it was accessed. Instead of sending the full resource, the server tells the client to use its cached copy.
How It Works
-
Initial Request: The client requests a resource from the server. If the server provides the resource, it includes headers such as
Last-ModifiedorETagthat help the client validate the cache. -
Subsequent Request: For future requests, the client includes headers like
If-Modified-SinceorIf-None-Matchto check if the resource has changed. -
Server Validation: The server compares these headers to the current resource state. If the resource hasn't changed, the server responds with a 304 status code, telling the client to use the cached version.
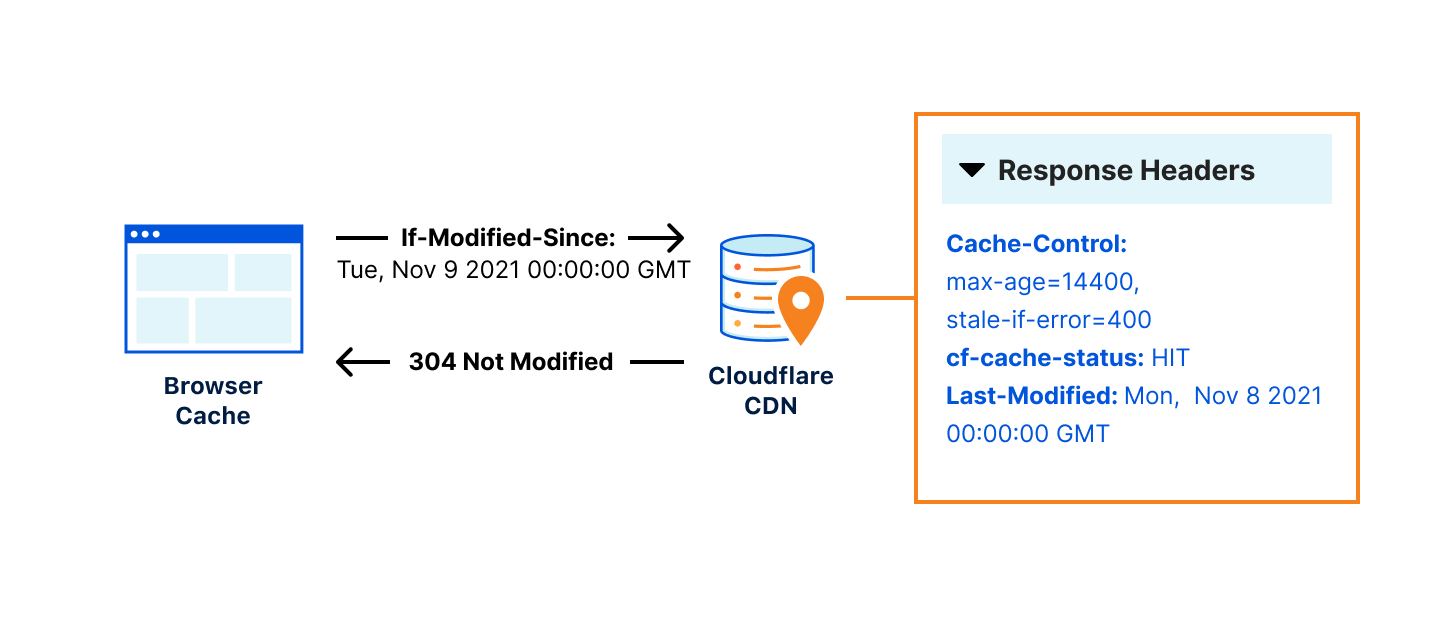
Benefits of 304 Responses
- Reduced Bandwidth: By avoiding sending unchanged resources, 304 responses save bandwidth.
- Improved Load Times: Clients can load resources faster from their cache rather than downloading them again.
- Lower Server Load: Servers handle fewer data transfers, reducing load and improving efficiency.
Cloudflare's Smart Edge Revalidation
Cloudflare enhances the traditional 304 revalidation process through Smart Edge Revalidation. This feature optimizes cache validation, ensuring more efficient use of cached resources.
How Smart Edge Revalidation Works
-
Initial Request: If your origin server includes
Last-ModifiedorETagheaders, Cloudflare respects and uses these headers for validation. If both of these headers are missing, Cloudflare automatically generates them to ensure effective revalidation. -
Revalidation Requests: For each request going through Cloudflare, we check if the request includes headers like
If-Modified-SinceorIf-None-Match. If they match theLast-ModifiedorETagheader values, we respond with a 304 Not Modified response code.
Note: When serving resources from Cloudflare’s cache, a stale resource might be revalidated using If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match headers. Cloudflare only performs revalidation if the origin server sends a Last-Modified or ETag header. Additionally, if the
Last-Modifiedheader was set by Cloudflare Cache, the ressources may not be revalidated. For more details, refer to Cloudflare Cache Responses.
Implementing 304 Responses with Cloudflare
To leverage 304 responses and Smart Edge Revalidation, ensure that your origin server is configured to not provide both the Last-Modified or ETag headers. This allows Cloudflare to automatically add the necessary headers for efficient cache validation.
If you want to disable Smart Edge Revalidation to fully control the behavior of the cache, you can configure you origin server to add one (or both) of these headers:
- ETag: A unique identifier for the resource that changes whenever the resource changes.
- Last-Modified: The date and time when the resource was last modified.
Note: When generated by Cloudflare, the
Last-Modifieddate can vary depending on which Cloudflare edge server responds to the request. Since each edge server operates independently and does not synchronize cache data, theLast-Modifieddate may not be the same across different edge servers.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Incorrect Headers: Ensure your server correctly sets
Last-ModifiedorETagheaders. - Cache Invalidation: Verify that changes to your content are appropriately invalidating the cache.
Debugging Tips
- Use browser developer tools to inspect HTTP headers and verify the presence of
If-Modified-SinceandIf-None-Matchin requests. - Check Cloudflare's cache analytics to monitor revalidation requests and cache hit/miss ratios.